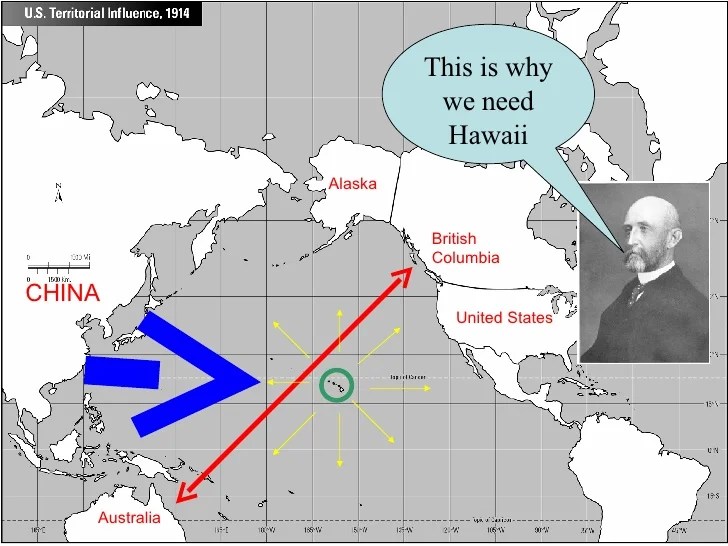
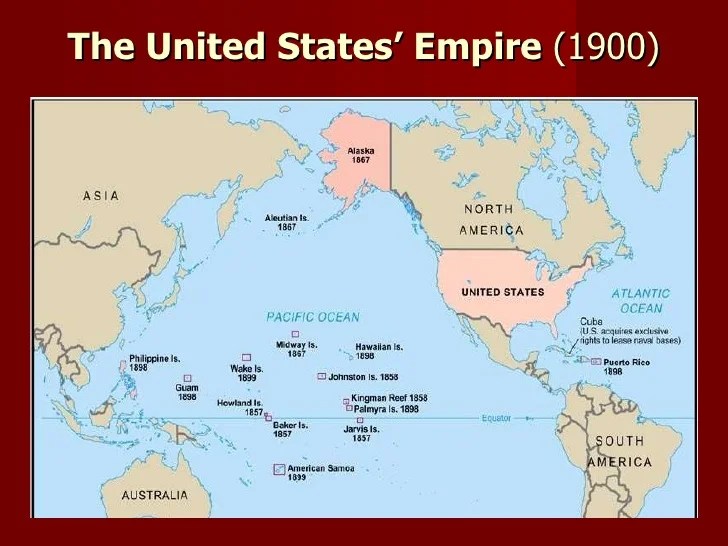
Us territorial influence 1914 map labeled – US Territorial Influence in 1914: A Labeled Map offers a comprehensive overview of the United States’ territorial expansion and its impact on the world. This map provides a visual representation of the extent of US influence, labeled with the dates of acquisition for each territory.
It serves as a valuable tool for understanding the historical context of US foreign policy and its geopolitical implications.
The map illustrates the vast reach of US territorial influence in 1914, spanning from the Pacific to the Caribbean. It includes territories acquired through various means, such as purchase, annexation, and military conquest. The map also highlights the role of key events, such as the Spanish-American War and the Panama Canal, in shaping US territorial expansion.
US Territorial Influence in 1914
In 1914, the United States possessed a vast territorial empire that spanned the globe. This empire included territories in North America, the Caribbean, the Pacific, and Asia. The US acquired these territories through a combination of conquest, purchase, and annexation.
The following map shows the extent of US territorial influence in 1914. The map is labeled with the dates of acquisition for each territory.

Factors Contributing to US Territorial Expansion, Us territorial influence 1914 map labeled
A number of factors contributed to US territorial expansion in the 19th and early 20th centuries. These factors included:
- Political factors:The US government believed that it had a duty to expand its territory in order to protect its citizens and to secure its borders. This belief was based on the idea of Manifest Destiny, which held that the US was destined to expand across the North American continent.
- Economic factors:The US economy was booming in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and this led to a demand for new land for agriculture, mining, and other industries.
- Social factors:Many Americans believed that it was their duty to spread their culture and values to other parts of the world. This belief was particularly strong among Protestant missionaries, who played a major role in the US expansion into the Pacific.
The Monroe Doctrine, which was proclaimed by President James Monroe in 1823, also played a role in US territorial expansion. The Monroe Doctrine stated that the US would not tolerate any further European colonization in the Americas. This doctrine gave the US a free hand to expand its own territory in the Western Hemisphere.
Impact of US Territorial Expansion
US territorial expansion had a profound impact on the Native American tribes that lived in the territories that were acquired by the US. Many tribes were forced to give up their land and move to reservations. Others were killed or assimilated into American society.
US territorial expansion also had a significant impact on the environment and natural resources. The US government often sold off public lands to private companies, which led to the destruction of forests, the extinction of species, and the pollution of rivers and lakes.
The geopolitical implications of US expansion were also significant. The US became a major world power, and its territorial acquisitions gave it a strategic advantage in the Pacific and the Caribbean.
US Territorial Influence in the Pacific
The US acquired a number of territories in the Pacific in the 19th and early 20th centuries. These territories included:
| Territory | Acquisition Date | Strategic Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Hawaii | 1898 | Pearl Harbor was a major naval base |
| Guam | 1898 | Guam was a coaling station for US ships |
| Philippines | 1898 | The Philippines were a major source of sugar and other agricultural products |
| Wake Island | 1899 | Wake Island was a strategic outpost in the Pacific |
| Midway Atoll | 1867 | Midway Atoll was a strategic outpost in the Pacific |
The US also acquired a number of other territories in the Pacific, including Samoa, the Aleutian Islands, and the Midway Islands. These territories gave the US a strategic advantage in the Pacific, and they played a major role in the US victory in World War II.
US Territorial Influence in the Caribbean
The US also acquired a number of territories in the Caribbean in the 19th and early 20th centuries. These territories included:
- Puerto Rico
- Cuba
- The Dominican Republic
- Haiti
- Panama
The US acquired these territories for a variety of reasons, including:
- To protect the Panama Canal
- To promote trade with Latin America
- To prevent other countries from gaining control of the Caribbean
The US policy of “dollar diplomacy” also played a role in the US acquisition of territories in the Caribbean. Dollar diplomacy was a policy of using economic pressure to influence the policies of other countries. The US used dollar diplomacy to force Cuba, the Dominican Republic, and Haiti to sign treaties that gave the US control over their finances and foreign policies.
Challenges to US Territorial Influence
The US faced a number of challenges to its territorial influence in the 20th century. These challenges included:
- Anti-colonial movements:Anti-colonial movements emerged in many of the US territories in the 20th century. These movements fought for independence from the US.
- The rise of nationalism:Nationalism also played a role in the decline of US territorial influence. Many people in the US territories began to identify with their own countries and cultures, rather than with the US.
- World War I:World War I weakened the US’s ability to maintain its territorial influence. The US was forced to divert its resources to the war effort, and it was unable to effectively control its territories.
As a result of these challenges, the US lost control of a number of its territories in the 20th century. These territories included the Philippines, Cuba, and Puerto Rico.
Commonly Asked Questions: Us Territorial Influence 1914 Map Labeled
What was the extent of US territorial influence in 1914?
In 1914, the US possessed a vast territorial empire that included the contiguous 48 states, Alaska, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. The US also had significant influence over Cuba, Panama, and other territories in the Caribbean and Pacific.
What were the factors that contributed to US territorial expansion?
The US’s territorial expansion was driven by a combination of political, economic, and social factors. Politically, the US sought to secure its borders and expand its sphere of influence. Economically, the US sought access to new markets and resources. Socially, the US was influenced by the ideology of Manifest Destiny, which held that the US had a divine right to expand westward across the continent.