Types of chemical reaction worksheet ch. 7 – Embark on a comprehensive exploration of chemical reactions with our meticulously crafted worksheet for Chapter 7. Delve into the intricacies of various reaction types, master the art of balancing equations, and unravel the secrets of reaction rates and equilibrium. This guide promises an immersive learning experience, equipping you with a profound understanding of the chemical world.
Types of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms and molecules to form new substances. There are various types of chemical reactions, each characterized by specific changes in the chemical composition and structure of the reactants and products.
The main types of chemical reactions include:
- Combination or synthesis reactions
- Decomposition reactions
- Single-displacement reactions
- Double-displacement reactions
- Combustion reactions
- Acid-base reactions
Chemical Equations
Chemical equations represent chemical reactions symbolically using chemical formulas. They provide information about the reactants, products, and stoichiometry (relative amounts) of the substances involved.
Balanced chemical equations ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. Balancing equations involves adjusting the coefficients (numbers in front of chemical formulas) to achieve this balance.
For example, the balanced equation for the combustion of methane (CH 4) is:
CH4+ 2O 2→ CO 2+ 2H 2O
Reaction Rates
Reaction rates measure the speed at which a chemical reaction proceeds. Factors that affect reaction rates include:
- Concentration of reactants
- Temperature
- Surface area of reactants
- Presence of a catalyst
- Nature of reactants
Equilibrium: Types Of Chemical Reaction Worksheet Ch. 7

Chemical equilibrium occurs when the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical reaction occur at the same rate, resulting in no net change in the concentrations of the reactants and products.
Equilibrium is a dynamic state, where the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time. Factors that affect equilibrium include:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Concentration of reactants and products
Acids and Bases

Acids and bases are substances that can donate or accept protons (H +ions), respectively.
Acids have a sour taste, turn blue litmus paper red, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
Bases have a bitter taste, turn red litmus paper blue, and react with acids to produce water and salt.
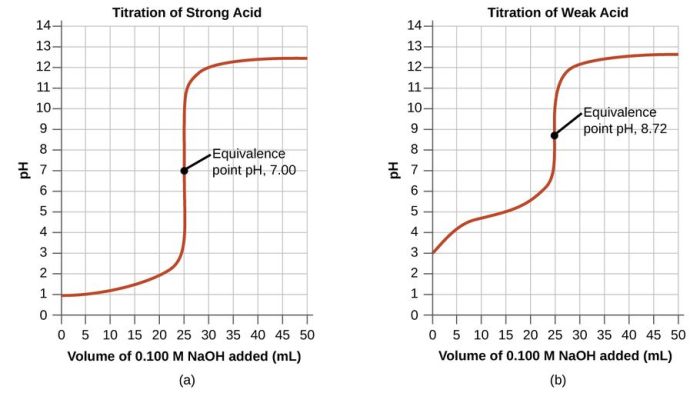
The strength of an acid or base is measured by its pH, which ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, while a pH below 7 indicates an acid and a pH above 7 indicates a base.
Redox Reactions
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions. Oxidation is the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons.
Redox reactions are important in many biological processes, such as respiration and photosynthesis.
In a redox reaction, the oxidizing agent (electron acceptor) causes the reduction of another substance, while the reducing agent (electron donor) causes the oxidation of the oxidizing agent.
Essential FAQs
What are the main types of chemical reactions?
The main types of chemical reactions include synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions.
How do I balance a chemical equation?
To balance a chemical equation, adjust the stoichiometric coefficients in front of each chemical formula until the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation.
What factors affect reaction rates?
Reaction rates are influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration, surface area, and the presence of a catalyst.