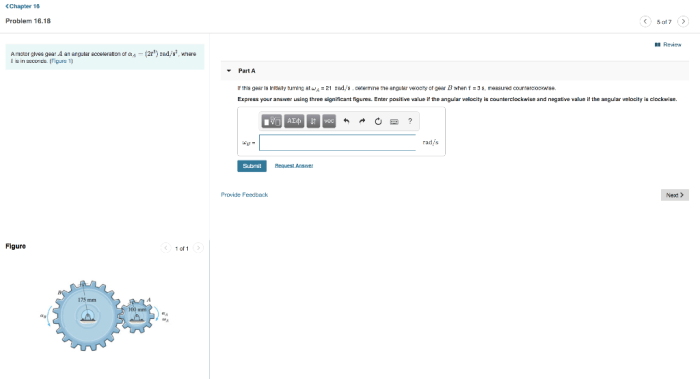
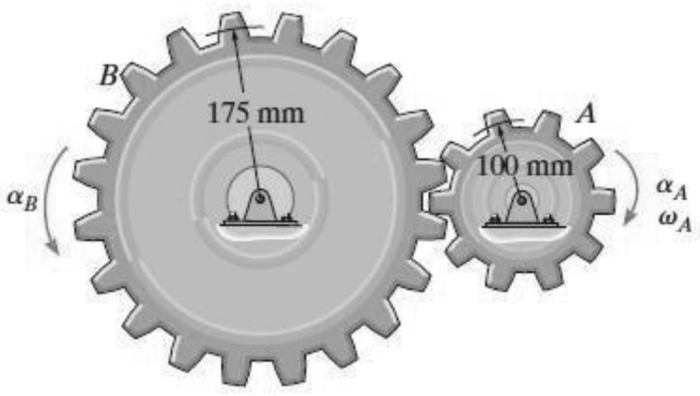
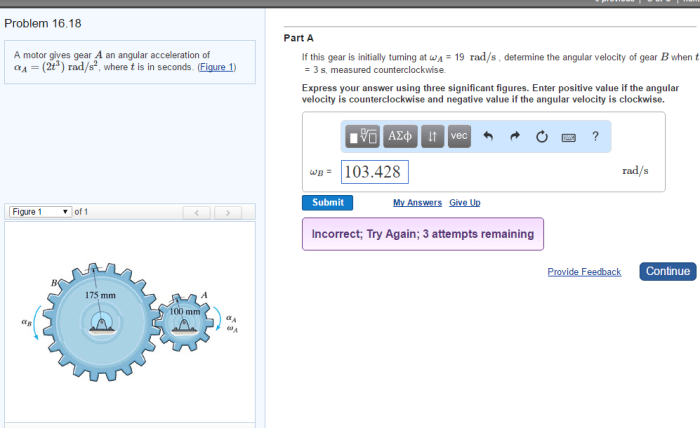
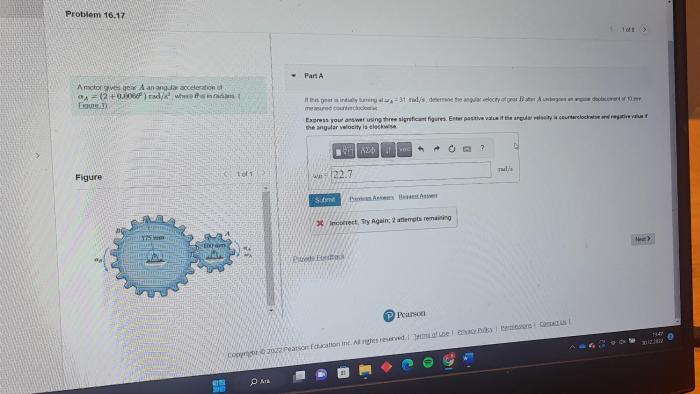
A motor gives gear a an angular acceleration of, a concept that plays a crucial role in various engineering applications. This article delves into the relationship between motors and gears, exploring how a motor’s torque and speed influence gear angular acceleration.
We will also examine the impact of gear design and material on angular acceleration, providing insights into selecting gears for specific requirements.
Understanding the principles of angular acceleration is essential for optimizing performance in industries such as manufacturing, robotics, and transportation. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, covering measurement techniques, troubleshooting common issues, and practical applications.
Definition of Angular Acceleration
Angular acceleration is a vector quantity that describes the rate at which an object’s angular velocity changes over time. It is measured in radians per second squared (rad/s 2).
The formula for angular acceleration is:
α = dω/dt
where:
- α is the angular acceleration (rad/s 2)
- ω is the angular velocity (rad/s)
- t is the time (s)
Angular acceleration can be positive or negative. A positive angular acceleration indicates that the object is rotating faster, while a negative angular acceleration indicates that the object is rotating slower.
Examples of angular acceleration in real-world scenarios include:
- The acceleration of a spinning top
- The acceleration of a rotating wheel
- The acceleration of a planet orbiting the sun
Relationship between Motor and Gear
A motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. A gear is a mechanical device that transmits motion and torque from one shaft to another. In a motor-gear system, the motor provides the torque and speed necessary to drive the gear.
The angular acceleration of a gear is directly proportional to the torque applied by the motor and inversely proportional to the gear’s moment of inertia.
α = T/I
where:
- α is the angular acceleration (rad/s 2)
- T is the torque (N·m)
- I is the moment of inertia (kg·m 2)
Gear Design and Material
The type of gear used in a motor-gear system depends on the specific application. Some common types of gears include:
- Spur gears
- Helical gears
- Bevel gears
- Worm gears
The material of the gear is also important. Gears can be made from a variety of materials, including:
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Plastic
- Bronze
The choice of material depends on the specific application and the required angular acceleration.
Applications of Angular Acceleration
Angular acceleration is a crucial factor in a wide range of practical applications, including:
- Manufacturing
- Robotics
- Transportation
In manufacturing, angular acceleration is used to control the speed of rotating machinery. In robotics, angular acceleration is used to control the movement of robotic arms. In transportation, angular acceleration is used to control the speed of vehicles.
Measurement and Analysis of Angular Acceleration: A Motor Gives Gear A An Angular Acceleration Of
There are a variety of methods for measuring angular acceleration, including:
- Tachometers
- Accelerometers
- Gyroscopes
Once angular acceleration has been measured, it can be analyzed to optimize performance. For example, in a manufacturing setting, angular acceleration data can be used to identify and correct problems with rotating machinery.
Troubleshooting Angular Acceleration Issues
There are a number of common problems that can affect angular acceleration, including:
- Motor-gear misalignment
- Gear wear
- Lubrication problems
These problems can be resolved by following a few simple troubleshooting steps.
- Inspect the motor-gear system for misalignment.
- Check the gears for wear and replace them if necessary.
- Lubricate the gears according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Top FAQs
What is angular acceleration?
Angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity over time. It is measured in radians per second squared (rad/s^2).
How does a motor affect gear angular acceleration?
A motor provides torque to the gear, which causes it to rotate. The motor’s torque and speed determine the gear’s angular acceleration.
What factors influence gear angular acceleration?
Gear design, material, and lubrication all influence gear angular acceleration. The number of teeth, tooth profile, and gear material affect the gear’s moment of inertia, which in turn affects its angular acceleration.