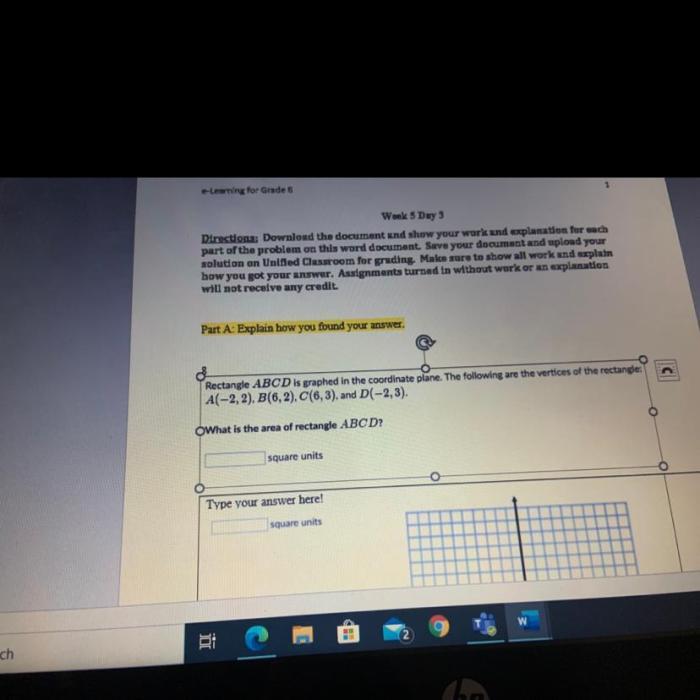
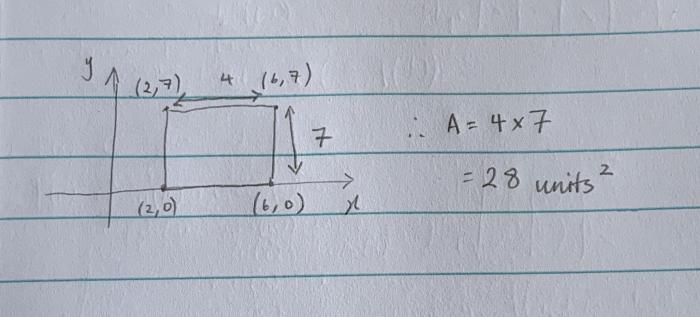Rectangle abcd is graphed in the coordinate plane – In the realm of geometry, the concept of a rectangle graphed in the coordinate plane holds significant importance. This geometric entity, denoted as rectangle ABCD, provides a framework for understanding various properties, transformations, and applications.
Delving into the intricacies of rectangle ABCD, we explore its fundamental properties, such as the calculation of side lengths, area, and perimeter. Additionally, we investigate the concept of a coordinate plane, which serves as a backdrop for plotting points and visualizing geometric figures.
Rectangle ABCD in the Coordinate Plane
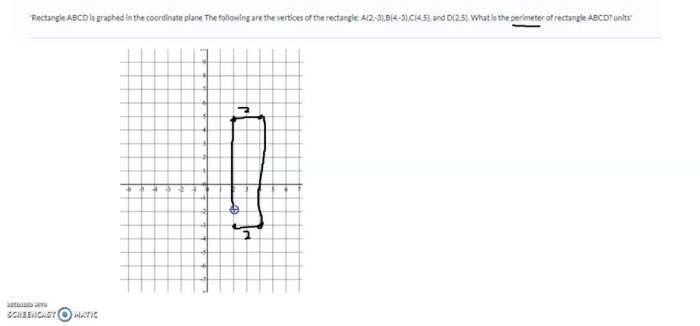
A rectangle is a two-dimensional shape with four straight sides and four right angles. It is a parallelogram with two pairs of parallel sides. Rectangle ABCD is graphed in the coordinate plane with vertices A(x1, y1), B(x2, y2), C(x3, y3), and D(x4, y4).
The coordinate plane is a two-dimensional plane that is divided into four quadrants by the x-axis and y-axis. The x-axis is the horizontal axis, and the y-axis is the vertical axis. The point (0, 0) is the origin of the coordinate plane.
To plot the points A, B, C, and D on the coordinate plane, we use their coordinates. For example, to plot point A, we start at the origin (0, 0) and move x1 units to the right along the x-axis.
Then, we move y1 units up along the y-axis. The point where we end up is point A.
Properties of Rectangle ABCD
- The length of side AB is x2 – x1.
- The length of side BC is y3 – y2.
- The length of side CD is x4 – x3.
- The length of side DA is y4 – y1.
- The area of rectangle ABCD is (x2 – x1) – (y3 – y2).
- The perimeter of rectangle ABCD is 2 – (x2 – x1) + 2 – (y3 – y2).
Rectangle ABCD is a square if and only if x2 – x1 = y3 – y2.
Transformations of Rectangle ABCD, Rectangle abcd is graphed in the coordinate plane
- To translate rectangle ABCD by a vector (a, b), we add a to the x-coordinate of each vertex and b to the y-coordinate of each vertex.
- To rotate rectangle ABCD by an angle θ about the origin, we use the following formulas:
- x’ = x – cos(θ) – y – sin(θ)
- y’ = x – sin(θ) + y – cos(θ)
- To reflect rectangle ABCD over the x-axis, we negate the y-coordinate of each vertex.
- To reflect rectangle ABCD over the y-axis, we negate the x-coordinate of each vertex.
- To dilate rectangle ABCD by a scale factor of k, we multiply the x-coordinate and y-coordinate of each vertex by k.
Applications of Rectangle ABCD
- Rectangles can be used to model real-world objects, such as a book, a window, or a door.
- Rectangles can be used to solve geometry problems, such as finding the area of a room or the perimeter of a garden.
- Rectangles can be used to design patterns and shapes, such as a checkerboard or a quilt.
- Rectangles can be used to create tessellations, which are patterns that cover a plane without any gaps or overlaps.
Essential Questionnaire: Rectangle Abcd Is Graphed In The Coordinate Plane
What is the significance of graphing rectangle ABCD in the coordinate plane?
Graphing rectangle ABCD in the coordinate plane allows for precise plotting and analysis of its properties, including side lengths, area, and perimeter.
How can rectangle ABCD be transformed in the coordinate plane?
Rectangle ABCD can undergo various transformations in the coordinate plane, such as translation, rotation, reflection, and dilation, which involve moving, rotating, flipping, or scaling the rectangle.
What are some real-world applications of rectangle ABCD?
Rectangle ABCD finds applications in modeling real-world objects, solving geometry problems, designing patterns and shapes, and creating tessellations.