Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1 Answers provides a comprehensive exploration of the fundamental principles and practical applications of neutralization titrations. This experiment is designed to enhance students’ understanding of acid-base reactions, equilibrium, and quantitative analysis. Through a series of guided steps and insightful explanations, this guide empowers learners to master the concepts and techniques involved in neutralization titrations, equipping them with a solid foundation for further studies in chemistry.
The experiment involves the titration of a known concentration of acid with a known concentration of base, using a pH indicator to determine the equivalence point. Students will learn how to calculate the concentration of the unknown acid or base using the titration data and explore the significance of the equivalence point in the titration process.
Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1
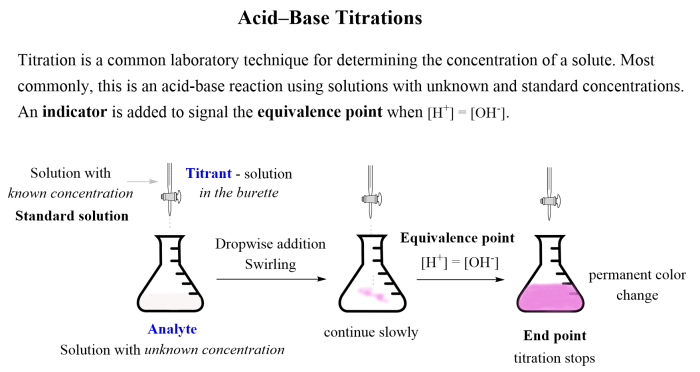
Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1 is designed to demonstrate the process of neutralization and to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. Neutralization is a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt and water.
The equivalence point in a neutralization titration is the point at which the moles of acid and base are equal. This experiment provides hands-on experience with titration techniques and reinforces the concept of neutralization.
Materials and Methods
- Burette
- Pipette
- Erlenmeyer flask
- Phenolphthalein indicator
- Unknown acid or base solution
- Sodium hydroxide solution (if titrating an acid)
- Hydrochloric acid solution (if titrating a base)
Procedure:
- Rinse the burette with the solution to be titrated.
- Fill the burette with the solution to be titrated.
- Pipette a known volume of the unknown acid or base solution into an Erlenmeyer flask.
- Add 2-3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the Erlenmeyer flask.
- Slowly add the solution from the burette to the Erlenmeyer flask, swirling constantly.
- Continue adding the solution from the burette until the solution in the Erlenmeyer flask turns a faint pink color.
- Record the volume of solution used from the burette.
Data Analysis, Experiment 22 neutralization titration 1 answers
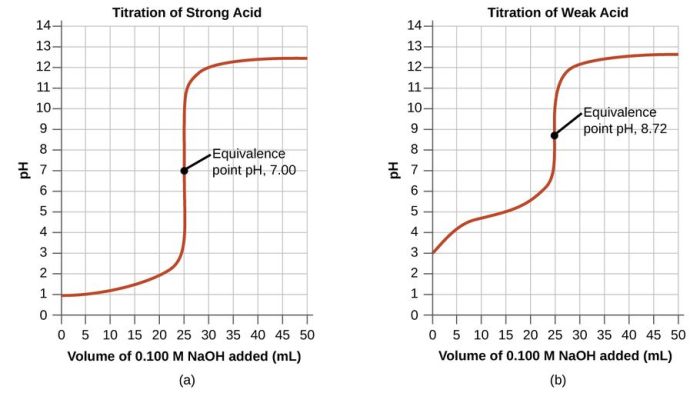
The equivalence point in the titration is the point at which the moles of acid and base are equal. This can be determined by plotting a graph of the pH of the solution versus the volume of solution added from the burette.
The equivalence point is the point at which the pH of the solution changes most rapidly.
The concentration of the unknown acid or base can be calculated using the following formula:
M1V1 = M2V2
where:
- M1 is the concentration of the known solution (sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid)
- V1 is the volume of the known solution used
- M2 is the concentration of the unknown solution
- V2 is the volume of the unknown solution used
Discussion
The equivalence point in a neutralization titration is the point at which the moles of acid and base are equal. This is an important concept in chemistry because it can be used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base.
There are a number of potential sources of error in a neutralization titration. These include:
- Inaccurate measurement of the volume of the solutions
- Incomplete reaction between the acid and base
- The presence of impurities in the solutions
These errors can be minimized by carefully following the procedure and using high-quality reagents.
The experimental results can be compared with expected values or theoretical calculations to assess the accuracy of the experiment.
FAQ Section: Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1 Answers
What is the purpose of Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1?
The purpose of Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1 is to provide students with a hands-on experience in conducting a neutralization titration, which is a fundamental technique used in chemistry to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base.
What are the key concepts covered in Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1?
Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1 covers key concepts such as acid-base reactions, neutralization, equivalence point, and quantitative analysis.
What equipment is required for Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1?
The equipment required for Experiment 22 Neutralization Titration 1 includes a buret, pipette, Erlenmeyer flask, pH indicator, and a known concentration of acid and base.