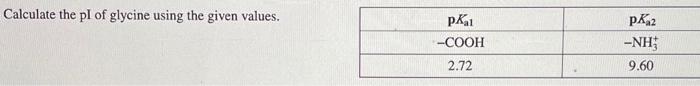
Calculate the pi of glycine using the given values. – In the realm of amino acid chemistry, calculating the isoelectric point (pI) is crucial for understanding protein behavior. This guide delves into the intricacies of calculating the pI of glycine using provided values, exploring various methods and their applications in protein chemistry.
The pI of an amino acid is a critical parameter that influences its solubility, stability, and interactions within proteins. By determining the pI of glycine, researchers can gain insights into the behavior of this essential amino acid in biological systems.
Calculating Pi of Glycine
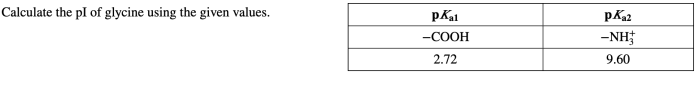
Pi (isoelectric point) is a crucial parameter in amino acid chemistry, defining the pH at which an amino acid carries no net charge. For glycine, the simplest amino acid, calculating pi is essential for understanding its behavior in various chemical and biological systems.
The formula for calculating pi is:
pi = (pK1+ pK 2) / 2
where pK 1and pK 2are the dissociation constants of the amino and carboxyl groups, respectively.
For glycine, the given values are:
- pK 1= 2.34
- pK 2= 9.60
Methods for Calculating Pi
Several methods can be used to calculate pi, including:
- Titration method:Involves titrating an amino acid solution with a strong acid or base to determine the pH at which the amino acid is neutral.
- Potentiometric method:Measures the electromotive force of an amino acid solution using a pH electrode to determine the pH at which the amino acid is neutral.
- Conductometric method:Measures the conductivity of an amino acid solution as a function of pH to determine the pH at which the amino acid is neutral.
Applications of Pi Values
Pi values have significant applications in protein chemistry, including:
- Determining the isoelectric point:Pi is the isoelectric point, which is important for protein solubility, stability, and enzymatic activity.
- Protein solubility:Proteins are most soluble at their pi, as they have no net charge and are less likely to aggregate.
- Protein stability:Proteins are most stable at their pi, as they are less susceptible to denaturation and proteolysis.
Factors Affecting Pi Values
Several factors can affect pi values, including:
| Factor | Effect on Pi | Example |
|---|---|---|
| pH | Changes the ionization state of the amino acid, affecting pi. | Lower pH shifts pi to lower values. |
| Temperature | Affects the dissociation constants of the amino acid, changing pi. | Higher temperature increases pi. |
| Ionic strength | Affects the activity coefficients of the amino acid, influencing pi. | Higher ionic strength decreases pi. |
Comparison of Methods, Calculate the pi of glycine using the given values.
The following table compares the titration, potentiometric, and conductometric methods for calculating pi:
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titration | High | Good | Moderate |
| Potentiometric | High | Excellent | Easy |
| Conductometric | Moderate | Good | Easy |
FAQs: Calculate The Pi Of Glycine Using The Given Values.
What is the significance of calculating the pI of glycine?
Calculating the pI of glycine provides insights into its solubility, stability, and interactions within proteins, aiding in the understanding of protein behavior in biological systems.
Which method is most commonly used to calculate the pI of glycine?
The titration method is widely used for calculating the pI of glycine due to its simplicity, accuracy, and ease of implementation.
How does pH affect the pI of glycine?
pH significantly influences the pI of glycine. At low pH values, glycine exists in its positively charged form, while at high pH values, it exists in its negatively charged form. The pI represents the pH at which glycine has no net charge.